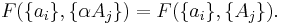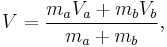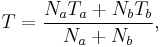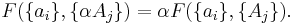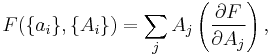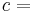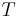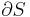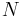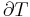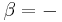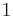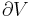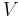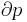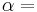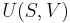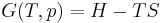Intensive and extensive properties
In the physical sciences, an intensive property (also called a bulk property, intensive quantity, or intensive variable), is a physical property of a system that does not depend on the system size or the amount of material in the system: it is scale invariant.
By contrast, an extensive property (also extensive quantity, extensive variable, or extensive parameter) is one that is additive for independent, noninteracting subsystems.[1] It is directly proportional to the amount of material in the system.
For example, density is an intensive property of a substance because it does not depend on the amount of that substance; mass and volume, which are measures of the amount of the substance, are extensive properties.
Note that the ratio of two extensive properties that scale in the same way is scale-invariant, and hence an intensive property.
Contents |
Intensive properties
An intensive property is a physical quantity whose value does not depend on the amount of the substance for which it is measured. For example, the temperature of a system in thermal equilibrium is the same as the temperature of any part of it. If the system is divided the temperature of each subsystem is identical. The same applies to the density of a homogeneous system: if the system is divided in half, the mass and the volume change in the identical ratio and the density remains unchanged.
According to the state postulate, for a sufficiently simple system, only two independent intensive variables are needed to fully specify the entire state of a system. Other intensive properties can be derived from the two known values.
Some intensive properties, such as viscosity, are empirical macroscopic quantities and are not relevant to extremely small systems.
Combined intensive properties
There are four properties in any thermodynamic system, two intensive ones and two extensive ones.
If a set of parameters, 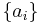 , are intensive properties and another set,
, are intensive properties and another set, 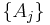 , are extensive properties, then the function
, are extensive properties, then the function 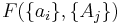 is an intensive property if for all
is an intensive property if for all 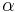 ,
,
It follows, for example, that the ratio of two extensive properties is an intensive property - density (intensive) is equal to mass (extensive) divided by volume (extensive).
Joining systems
Let there be a system or piece of substance a of amount ma and another piece of substance b of amount mb which can be combined without interaction. [For example, lead and tin combine without interaction, but common salt dissolves in water and the properties of the resulting solution are not a simple combination of the properties of its constituents.] Let V be an intensive variable. The value of variable V corresponding to the first substance is Va, and the value of V corresponding to the second substance is Vb. If the two pieces a and b are put together, forming a piece of substance "a+b" of amount ma+b = ma+mb, then the value of their intensive variable V is:
which is a weighted mean. Further, if Va = Vb then Va + b = Va = Vb, i.e. the intensive variable is independent of the amount. Note that this property holds only as long as other variables on which the intensive variable depends stay constant.
In a thermodynamic system composed of two monatomic ideal gases, a and b, if the two gases are mixed, the final temperature T is
a weighted mean where 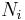 is the number of particles in gas i, and
is the number of particles in gas i, and 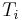 is the corresponding temperature.
is the corresponding temperature.
Note that you have to measure the amounts in the same unit that was used to calculate the intensive property from the extensive property. So when you interpolate density, you have to measure the properties in volume, as density is mass per volume. The formula makes no sense when you measure the properties in mass (kg).
Examples
Examples of intensive properties include:
- temperature
- chemical potential
- density (or specific gravity)
- viscosity
- velocity
- electrical resistivity
- spectral absorption maxima (in solution)
- specific energy
- specific heat capacity
- hardness
- melting point and boiling point
- pressure
- ductility
- elasticity
- malleability
- magnetization
- concentration
Extensive properties
An extensive property is defined by the IUPAC Green Book as a physical quantity which is the sum of the properties of separate noninteracting subsystems that compose the entire system.[1] The value of such a property is proportional to the size of the system it describes, or to the quantity of matter in the system.
Extensive properties are the counterparts of intensive properties, which are intrinsic to a particular subsystem. Dividing one type of extensive property by a different type of extensive property will in general give an intensive value. For example, mass (extensive) divided by volume (extensive) gives density (intensive).
Combined extensive properties
If a set of parameters 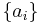 are intensive properties and another set
are intensive properties and another set 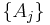 are extensive properties, then the function
are extensive properties, then the function 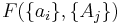 is an extensive property if for all
is an extensive property if for all 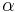 ,
,
Thus, extensive properties are homogeneous functions (of degree 1) with respect to 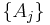 . It follows from Euler's homogeneous function theorem that
. It follows from Euler's homogeneous function theorem that
where the partial derivative is taken with all parameters constant except 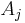 . The converse is also true - any function which obeys the above relationship will be extensive.
. The converse is also true - any function which obeys the above relationship will be extensive.
Examples
Examples of extensive properties include:
Related extensive and intensive properties
Although not true for all physical properties, there are a number of properties which have corresponding extensive and intensive analogs, many of which are thermodynamic properties. Examples of such extensive thermodynamic properties, which are dependent on the size of the thermodynamic system in question, include volume (V), internal energy (U), enthalpy (H), entropy (S), Gibbs free energy (G), Helmholtz free energy (A), and heat capacities (Cv and Cp) (in the sense of thermal mass). Note that the main symbols of these extensive thermodynamic properties shown here are capital letters. Except for volume (V), these extensive properties are dependent on the amount of material (substance) in the thermodynamic system in question.
For homogeneous substances, these extensive thermodynamic properties each have analogous intensive thermodynamic properties, which can be expressed on a per mass basis, and the corresponding intensive property symbols would be the lower case letters of the corresponding extensive property. Examples of intensive thermodynamic properties, which are independent on the size of the thermodynamic system in question and are analogous to the extensive ones mentioned above, include specific volume (v), specific internal energy (u), specific enthalpy (h), specific entropy (s), specific Gibbs free energy (g), specific Helmholtz free energy (a), and specific heat capacities (cv and cp, sometimes simply called specific heats). These intensive thermodynamic properties are effectively material properties which are valid at a point in a thermodynamic system or at a point in space at a certain time. These intensive properties are dependent on the conditions at that point such as temperature, pressure, and material composition, but are not considered dependent on the size of a thermodynamic system or on the amount of material in the system. See the table below. Specific volume is volume per mass, the reciprocal of density which equals mass per volume.
| Extensive property |
Symbol | SI units | Intensive property** |
Symbol | SI units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume |
|
|
Specific volume*** |
|
|
| Internal energy |
|
|
Specific internal energy |
|
|
| Entropy |
|
|
Specific entropy |
|
|
| Enthalpy |
|
|
Specific enthalpy |
|
|
| Gibbs free energy |
|
|
Specific Gibbs free energy |
|
|
| Heat capacity at constant volume |
|
|
Specific heat capacity at constant volume |
|
|
| Heat capacity at constant pressure |
|
|
Specific heat capacity at constant pressure |
|
|
- * l = liter, J = joule
- ** specific properties, expressed on a per mass basis
- *** Specific volume is the reciprocal of density.
If a molecular weight can be assigned for the substance, or the number of moles in the system can be determined, then each of these thermodynamic properties can be expressed on a per mole basis. These intensive properties could be named after the analogous extensive properties but with the word "molar" preceding them; thus molar volume, molar internal energy, molar enthalpy, molar entropy, etc. Although the same small letters can be used as in the analogous specific properties indicating they are intensive, sometimes the corresponding capital letters have been used (and understood to be on a per mole basis), and there seems to be no universally agreed upon symbol convention for these molar properties. A well known molar volume is that of an ideal gas at STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure); this molar volume = 22.41 liters per mole. Molar Gibbs free energy is commonly referred to as chemical potential, symbolized by μ, particularly when discussing a partial molar Gibbs free energy μi for a component i in a mixture.
Counter-example
There are measured physical properties which are neither intensive nor extensive. For example the electrical resistance of two resistors is the sum of their two resistances only if the resistors are connected in series, but not if they are connected in parallel. The electrical resistance of independent noninteracting resistors (subsystems) is therefore not additive in general, and electrical resistance is not an extensive property. Nor is it intensive because the resistance of the two resistors is not equal in general, even if they consist of the same material at the same temperature and pressure.
References
- Callen, Herbert B. (1985). Thermodynamics and an Introduction to Themostatistics (2nd Ed. ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-86256-8.
- Lewis, G.N.; Randall, M. (1961). Thermodynamics (2nd Edition ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company.
- ^ a b IUPAC Green Book Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry (3rd edn. 2007), page 6 (page 20 of PDF file)